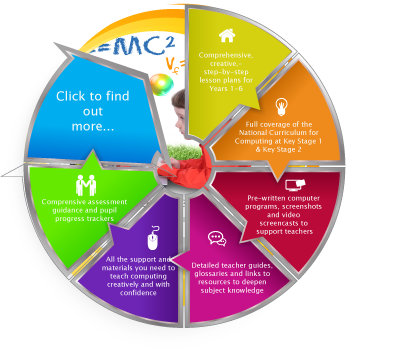
Have you got it covered?
The primary computing curriculum has now been statutory since September 2014 with the introduction of the National Curriculum for Computing at Key Stage 1 and Key Stage 2. All schools should now be teaching a broad and balanced computing curriculum that provides full curriculum coverage of the aims and objectives of the National Curriculum for Computing. But are they?

Think you’re “doing” Computing?
There seems to be a wealth of resources available now to help teachers teach computing. There’s lots of stuff online. Even better, free stuff! Gather all that; organise it (roughly) into year groups and that’s Computing sorted!
The trouble is, most of it is targeted to help schools in only one aspect of the computing curriculum: coding. And Computing is so much more than just coding.
School’s really don’t have it covered if that’s all they’re doing. Or, even, if they’re doing some bits on eSafety too; or one lesson about networks before falling back to those old ICT units (Word processing, Spreadsheets and good-old Powerpoint) that someone – now long gone from the school – put together from the QCA ICT scheme of work back in 2000. Or, even, if they bought a scheme adapted from an old ICT scheme with about twelve extra lessons on coding added in. Schools are being let down. More importantly, they’re letting pupils down.
In what other subject is it okay for teachers to admit they know nothing about the subject they teach? To proffer copying answers and children teaching each other as the only pedagogical approaches? In what other profession would teachers offer support and training whilst freely admitting you know very little? Would it be acceptable for a maths coordinator to miss out all of the bits of maths they don’t understand? Or teach from outdated materials? – ‘Look, I don’t really like that the government want us to teach graphs and algebra and some other hard bits and I’ve got some really good stuff on counting with an abacus that I found on Wikipedia via the Ancient Chinese so I’m going to do that all year instead’.
I don’t care whose materials schools use or who helps teachers, as long as they’re good because what I do, passionately, care about is that children are taught computing well. And I don’t think they are. Most schools aren’t teaching it properly. Schools need to give computing the status and comprehensive coverage it deserves.
The three strands of computing are:
- Computer Science
- Digital Literacy (incl. eSafety)
- Information Technology
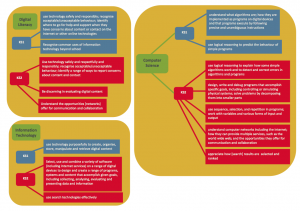
Click to download iCompute’s breakdown of computing strands against NC objectives for primary computing
According to Ofsted inspection guidance for Computing:
Teaching
For Good or Better teaching, teachers have an enthusiasm and passion for computing. Teachers use a wide variety of innovative and imaginative resources and teaching techniques.
Subject knowledge is excellent, continually up-to-date and demonstrates a high level of technical expertise.
Curriculum
The curriculum is broad and balanced and covers all three strands of computing. It is imaginative, stimulating, progressive and set in contexts meaningful to the children.
Children use their knowledge, skills and understanding in realistic and challenging situations. Pupils have comprehensive knowledge and understanding about how to stay safe when using new technologies.
Subject Leadership
High levels of subject expertise and vision with a strong record of innovation in computing. CPD is well-targeted.
Access to computing equipment is outstanding and the school is likely to have promoted the use of mobile technologies.
There is an engaging, age-appropriate e-safety curriculum in place.
E-safety is a priority within the school and promoted throughout. Staff receive regular training and rigorous policies are in place.
How are you doing?

Reflective Practitioner
Children have a statutory entitlement to a high-quality computing education. I encourage you to reflect on the practice and provision within your school.
In doing so, here are some questions you could use as a basis for reflection:
Staff
Do all staff have:
- good or better subject knowledge?
- good or better subject pedagogy?
- the ability and time to develop comprehensive, progressive, computing curricula?
- high expectations of learning in computing?
Curriculum
Do you have a computing curriculum that:
- provides full coverage of the National Curriculum for Computing at Key Stage 1 & 2?
- is broad, balanced and meets the needs of all learners?
- is engaging and inclusive?
- uses a rich and varied range of software, tools and technologies?
- supports teaching and learning with comprehensive assessment guidance?
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save
Save